9 GitHub Open-Source Projects for AI – Controlled Computers
01 Control Your Computer via Terminal
Install this open – source project on your computer, and your terminal will turn into Jarvis. This 61K – star open – source project enables computer control right from your terminal.
Open Interpreter is an interpreter that allows large AI models to run code locally. It supports running Python, JavaScript, Shell, and other programming languages, and operates directly within your terminal.
By conversing with it, you can access the Internet—not just Bing Search, but unrestricted web access.
It can handle local files, such as batch renaming, format conversion, and Excel processing. It can also control your computer, like opening browsers, sending emails, and even adjusting system settings.
Local model integration is also supported, including Ollama and Jan.
For example, input: Set my system to dark mode and then open a browser to check tomorrow’s weather.
It will execute Shell commands to modify system settings and use browser automation tools like Selenium or Playwright to fetch the information.
You can also feed it a 500MB Excel spreadsheet and command: Analyze this spreadsheet, plot the sales trend over the past year, and save it as report.png.
No cloud upload is required, ensuring absolute data privacy and security.
Open – Source Repository: https://github.com/openinterpreter/open-interpreter
02 Microsoft Open Source: OmniParser
OmniParser is a powerful open – source tool developed by Microsoft specifically for screen parsing.
Its latest V2 version, released this year, has topped the Hugging Face charts for a long time, significantly elevating the capabilities of GUI Agents.
It is a screen parsing tool that converts screenshots into structured data, serving as a core component for building AI – powered computer – controlling Agents.
Many vision – based automation projects rely on such technology for accurate screen element localization.
Its workflow is as follows:
- Detect: Pre – trained YOLO models accurately frame all interactive elements on the screen, including buttons, input fields, icons, and sidebars.Even tiny icons can be precisely captured by the V2 version.
- Caption: Microsoft’s own Florence – 2 or BLIP – 2 models are used to add functional descriptions to each framed element, e.g., “This is a search icon” or “This is a settings button”.
- Grounding: These coordinates and descriptions are fed to models like GPT – 4V or DeepSeek, enabling the large model to know that a button is located at coordinates (800, 600).
You can think of this open – source project as a pair of high – precision glasses connecting the large model “brain” to the computer screen.
Open – Source Repository: https://github.com/microsoft/OmniParser
03 Self – Operating Computer Framework
This open – source framework also enables multimodal AI models to operate computers like humans. It has now gained 10,000 stars on GitHub.
The model visually recognizes on – screen content via screenshots and directly interacts using the system’s mouse and keyboard interfaces with the pyautogui library, rather than relying on backend APIs GitHub.
Moreover, this open – source project is compatible with macOS, Windows, and Linux GitHub.
To address issues where large models may misidentify or misclick screen elements, several key modes have been introduced:
- OCR Mode: Generates a coordinate hash map of clickable elements on the screen. When the model decides to click on specific text, the system can accurately map it to exact coordinates, greatly improving click accuracy.
- Set – of – Mark (SoM) Prompt: Adds numerical labels to UI elements in screenshots, allowing the model to locate elements by simply outputting numbers—similar to the visual annotation logic used in Tesla’s autonomous driving.
- Voice Mode: Supports voice input commands for enhanced interaction convenience.
Open – Source Repository: https://github.com/OthersideAI/self-operating-computer
04 Cutting – Edge GUI Agent: Agent S
Agent S is one of the most advanced open – source GUI agent frameworks available today. Its S3 model was the first to surpass human – level performance on OSWorld, achieving a score of 72.60%.
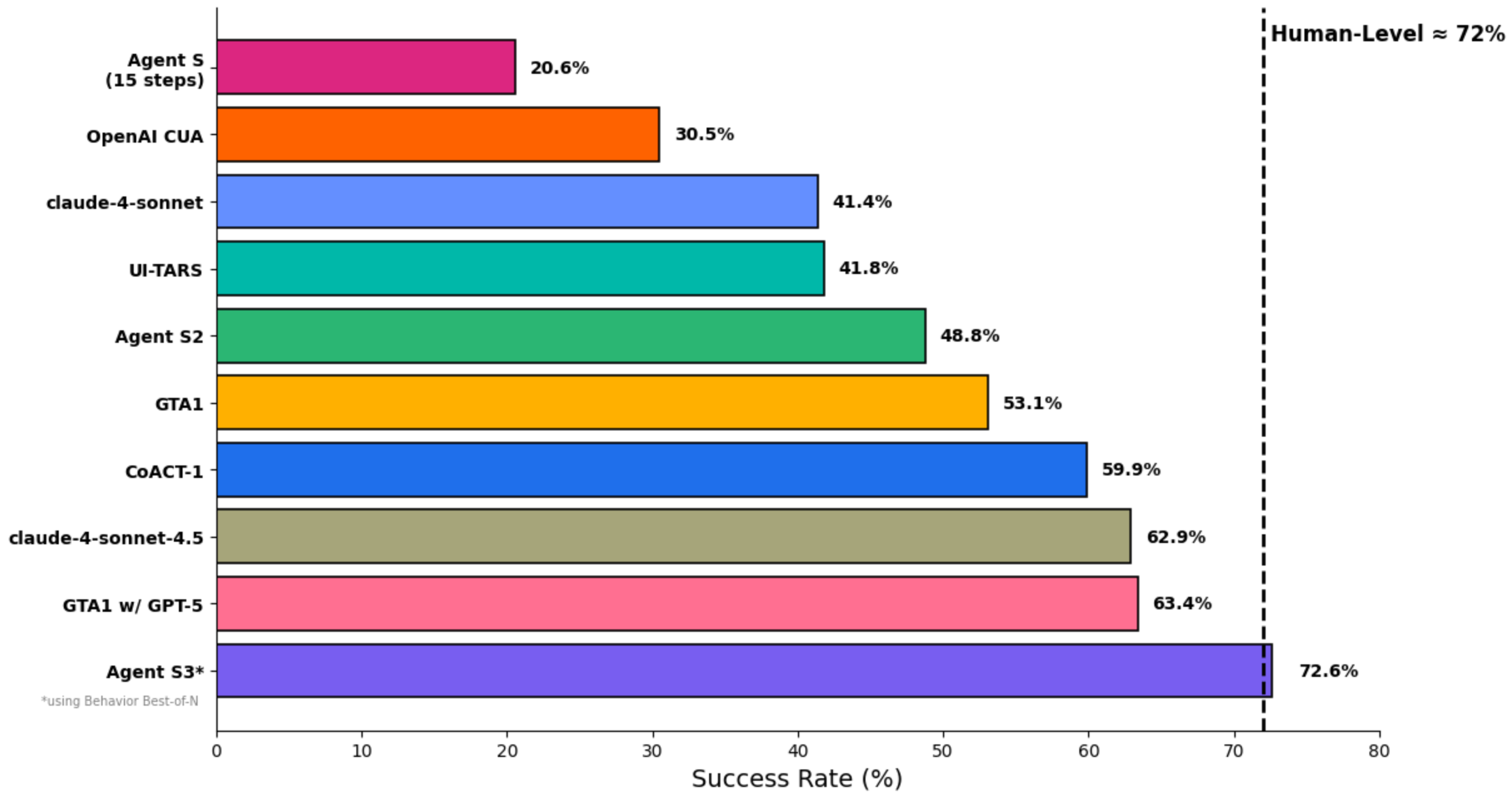
It has accumulated 9,000 stars on GitHub so far.
Unlike regular scripts, Agent – S incorporates a human – like cognitive architecture:
- Experience – Enhanced Hierarchical Planning: Instead of acting blindly step – by – step, it first searches for external knowledge (e.g., online tutorials) and retrieves internal memory to break down large tasks into subtasks.
- Agent – Computer Interface: It does not directly process raw pixels but perceives GUI elements more accurately through an intermediate layer, enhancing the model’s understanding of the screen.
- Dual – Memory Mechanism: Episodic memory stores high – level task experiences, while situational memory keeps track of specific operational steps. The more it is used, the better it becomes at handling complex tasks.
Open – Source Repository: https://github.com/simular-ai/Agent-S
05 Microsoft Open Source: UFO
As previously mentioned, UFO is another open – source framework from Microsoft.
This open – source project is a native – level agent system tailored specifically for the Windows ecosystem. Leveraging Microsoft’s in – depth understanding of its own system, it achieves more in – depth control than regular vision – based solutions.
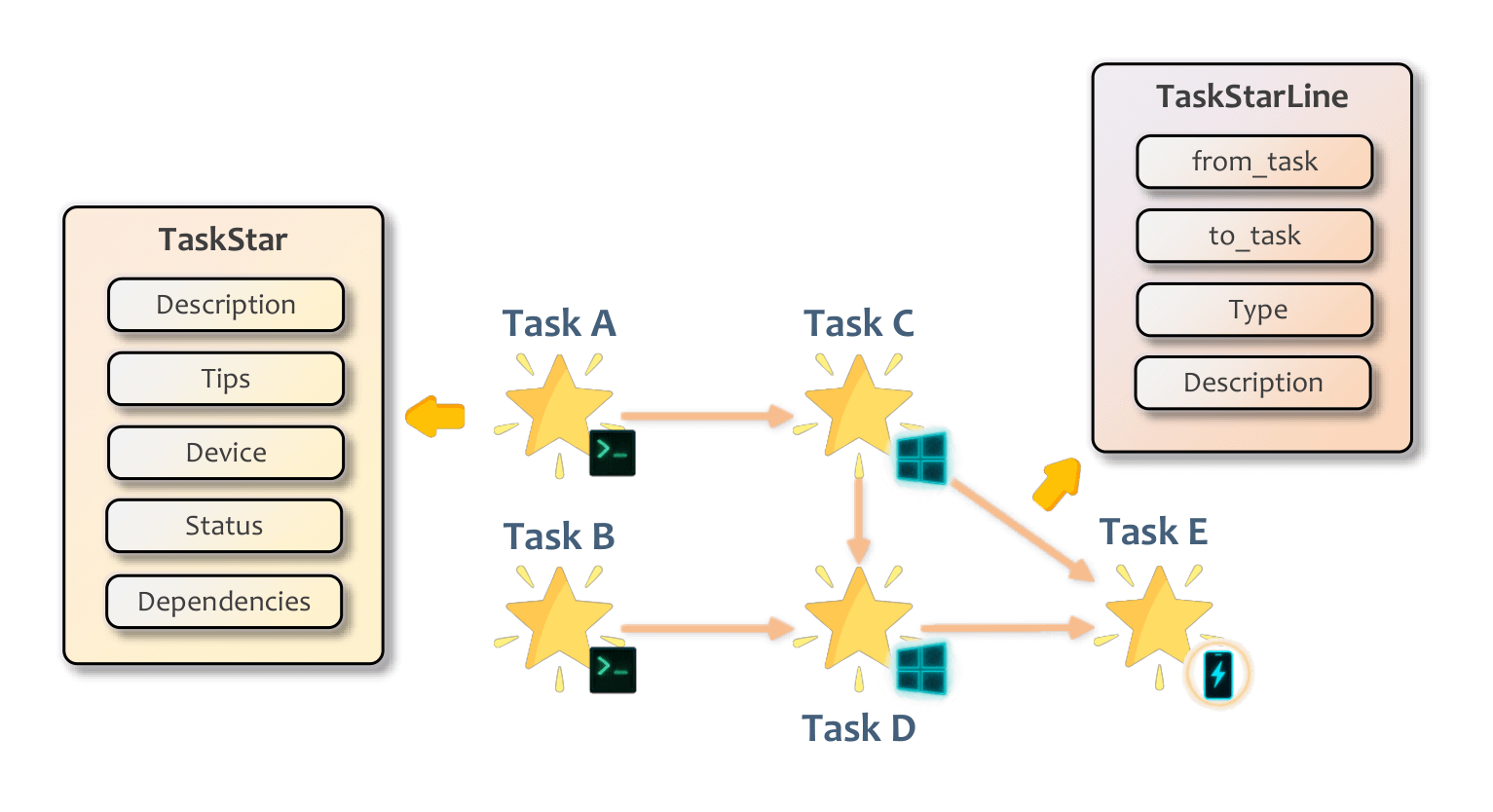
Unlike vision – only frameworks that rely solely on screenshots and mouse simulation, UFO combines vision with underlying system interfaces such as Windows UI Automation, Win32, and COM API.
It not only “sees” the screen but also directly reads the control tree. It can accurately identify a button’s name, status, and hidden properties, ensuring an extremely high click accuracy rate.
Additionally, it has been optimized for commonly used Windows software, including the Microsoft Office suite and File Explorer, enabling it to understand the internal logic of applications.
It adopts a dual – agent architecture (AppAgent and OSWorld Agent) to deeply understand the UI structure of Windows applications and execute complex cross – application requests, such as extracting content from a PPT and sending it via email.
Optimized specifically for Windows, it leverages native Windows APIs for more stable control.
Open – Source Repository: https://github.com/microsoft/UFO
06 AI Playing Red Dead Redemption
Cradle is an open – source project developed by the Beijing Academy of Artificial Intelligence (BAAI) team.
It allows AI agents to operate any software and games like humans, using only screenshots for input and standard keyboard/mouse for output—no reliance on backend APIs or internal code access.
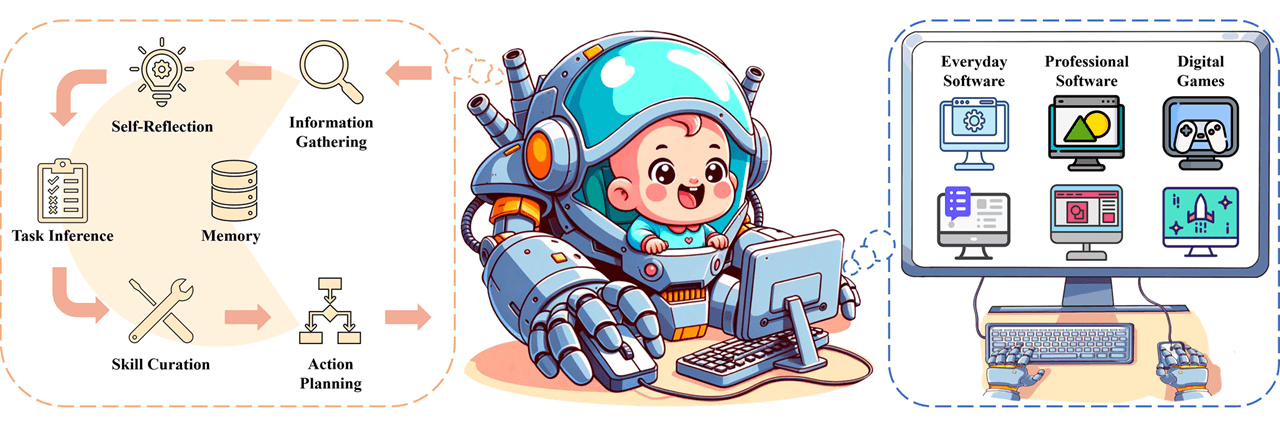
It can be used to play games such as Red Dead Redemption and Cities: Skylines, as well as operate software like Lark, Chrome, and CapCut.
It provides a standardized framework that divides the control process into several key modules:
- Perception: Extracts key information from the screen, identifying UI interfaces, icons, text, or 3D scenes in games.
- Decision – Making and Planning: Plans the next actions based on current task objectives and screen status. It engages in self – reflection, analyzing failures to revise strategies if operations go wrong.
- Memory System: Short – term memory records recent operation sequences and screenshots; long – term memory stores successful experiences and tool usage manuals (RAG) for quick retrieval in similar scenarios.
- Execution: Converts plans into specific keyboard and mouse commands.
Open – Source Repository: https://github.com/BAAI-Agents/Cradle
07 OS – Copilot
OS – Copilot is a framework for building universal operating system agents. It emphasizes the agents’ ability of self – learning and self – improvement, enabling them to handle unfamiliar applications.
Its core agent, FRIDAY, can learn to operate Excel, PPT, and browse the web through self – improvement mechanisms.
The goal of this open – source project is to create a personal assistant that seamlessly integrates into the operating system.
Open – Source Repository: https://github.com/OS-Copilot/OS-Copilot
08 ShowUI
ShowUI is a lightweight end – to – end Vision – Language – Action (VLA) model designed specifically for GUI agents.

It aims to solve the problems of high latency and computational costs when large models handle UI interfaces, providing faster and more accurate screen element localization and control.
The model is compact and efficient, making it suitable for local deployment to achieve low – latency UI automation control.
Open – Source Repository: https://github.com/showlab/ShowUI
09 UI – TARS Desktop
As previously introduced, UI – TARS Desktop is an open – source GUI agent desktop application developed by ByteDance, based on the UI – TARS vision – language model.

It allows users to directly control Windows or macOS computers using natural language.
Combining an end – to – end vision model, this project eliminates the need for complex intermediate code parsing. Instead, it “sees” the screen and operates the mouse and keyboard just like humans.
It features out – of – the – box functionality and supports remote computer control, representing one of the latest high – performance GUI Agent implementations.
Open – Source Repository: https://github.com/bytedance/UI-TARS-desktop